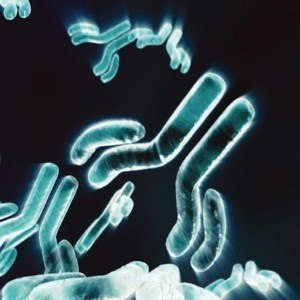
As of today, there are a total of 367 monoclonal antibodies either on the market or in development. 124 are fully human, 146 are humanized, 37 are chimeric, and 56 are murine, or mice antibodies. Of these 367, 38 are FDA approved since the first got through in 1986. 16 of those 38 have been approved in the last 5 years alone, which translates to 42%. We are gaining traction quickly, it seems.
Of the 38 approved mabs, 18 are humanized, 14 are fully human, 7 are chimeric, and only one is murine. The difference between the types is this: A chimeric mab is a cross between an animal and a human antibody engineered to react in a human setting. Humanized means that the antibody is mostly converted into a human form but originally came from an animal, usually a mouse. The term "fully human antibody" though is actually a bit misleading because in almost all cases it is not actually taken from a human. It is generally taken from a mechanism called a phage display, where human antibody genes are injected into a phage virus, which then expresses the antibodies on its coat. The best ones are then harvested from the virus. Think of it as microbiological agriculture.
Zooming back out to mabs in general, the top 10 bestselling mabs in 2014 account for $68B of the $78B total mab market last year. Number 1 is the fully human adalimumab, or Humira for rheumatoid arthritis, which looks set to eventually overtake Lipitor as the biggest blockbuster drug of all time. Humira was discovered via phage display, along with (nearly) all other fully human mabs on the market or in development.
Via Krishan Maggon



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...







Humira was the best selling human medicinal brand in 2014 but will be overtaken by Gilead Hepatitis C antiviral sofosbuvir and Harvoni.