Science Codex In space, astronauts' immune systems get totally confused Washington Post "If this situation persisted for longer deep space missions, it could possibly increase risk of infection, hypersensitivity, or autoimmune issues for...
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
Resources and Material for Lecturers and Students - Immunology (University level)
Curated by
Alfredo Corell
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|






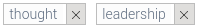

But it isn't certain that these changes would significantly increase the risks of long-term spaceflight. An upcoming year-long mission will provide further data for study. If the evidence suggests that immune system confusion could pose a threat to astronauts, the next step will be figuring out how to counteract it. Whatever they develop could make its way back to earth, providing new tools to help immune-compromised patients here at home.
Original Manuscript at the Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research
DOI: 10.1089/jir.2013.0129
http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/pdf/10.1089/jir.2013.0129